Quick Start
Installation
You can specify to install it through pip.
pip install -U pykt-toolkit
We advise to create a new Conda environment with the following command:
conda create --name=pykt python=3.7.5
source activate pykt
pip install -U pykt-toolkit
Train Your First Model
Prepare a Dataset
1、Obtain a Dataset
Let’s start by downloading the dataset from here. Please make sure you have creat the data/{dataset_name} folder
2、Data Preprocessing
python data_preprocess.py [parameter]
Args:
--dataset_name: dataset name, default=“assist2015”
--min_seq_len: minimum sequence length, default=3
--maxlen: maximum sequence length, default=200
--kfold: divided folds, default=5
Example:
cd examples
python data_preprocess.py --dataset_name=ednet
Training a Model
After the data preprocessing, you can use the python wandb_modelname_train.py [parameter] to train a model:
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=2 nohup python wandb_sakt_train.py --dataset_name=assist2015 --use_wandb=0 --add_uuid=0 --num_attn_heads=2 > sakt_train.txt &
Evaluating Your Model
Now, let’s use wandb_predict.py to evaluate the model performance on the testing set.
python wandb_predict.py
Args:
--bz: batch_size, default is 256
--save_dir: the dictory of the trained model, default is "saved_model"
--fusion_type: the fusion mode,default is "late_fusion"
--use_wandb: use wandb or not, default is 1
Evaluation Protocol
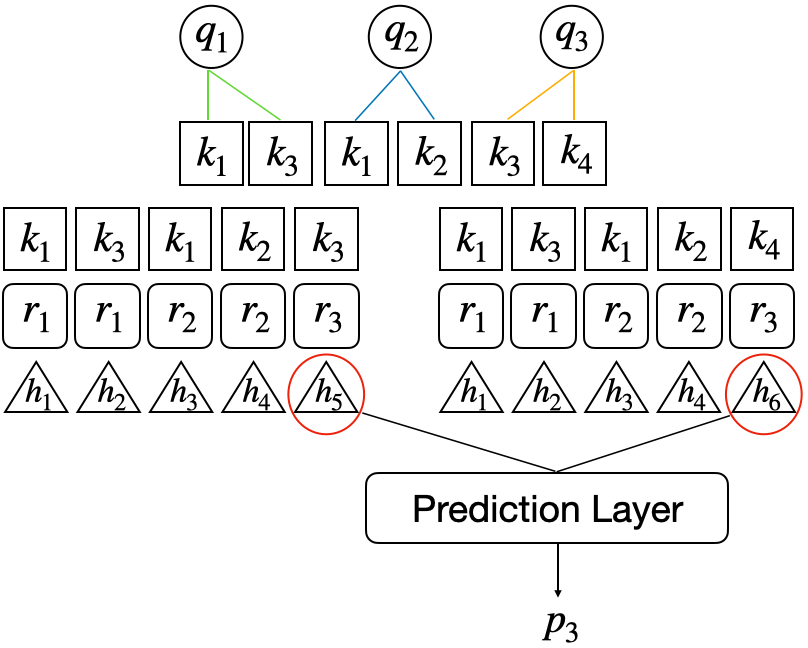
A question may be related to multiple knowledge concepts (KCs). To make the evaluation of pyKT is consistent with the real-world prediction scenarios, we train DLKT models on KCs but evaluate them on questions level as follows:
Early fusion: Calculate the average of the hidden states on KC levels, and then input the average results into the prediction layer, hence get the prediction results on question level. For example, to obtain the prediction $p_3$ of $q_3$, we average the hidden states $h_5,h_6$ into the prediction layer.
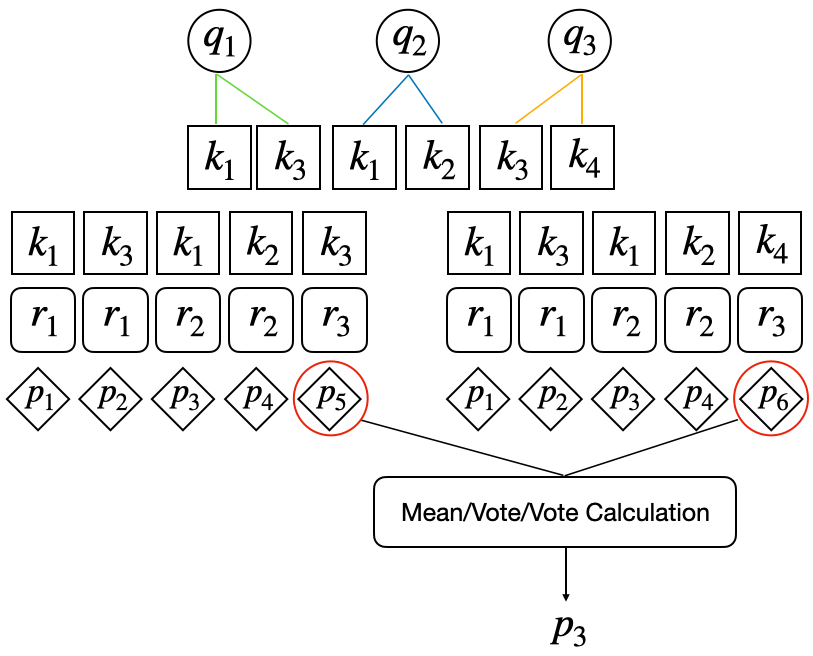
Late fusion: Employ three fusion types to obtain the question-level prediction based on the KC-level prediction results:(1) Mean: compute the average of the KC-level prediction results as the final prediction. (2) Vote: select half of the values of KC predictions as the final prediction. (3) All: only if all KC predictions are correct, the final prediction is correct, otherwise it is wrong.
Hyperparameter Tuning
Create a Wandb Account
We use Weights & Biases (Wandb) for hyperparameter tuning, it is a machine learning platform for developers to build better models faster with experiment tracking. Firstly, let’s register an account in Wandb webpage to get the API key from here:
Next, add your uid and api_key into configs/wandb.json.
Sweep Configuration
[wandb_key] python generate_wandb.py [parameter]
Args:
--src_dir: The parameter configuration file path of the model
--project_name: Project name on wandb, default: kt_toolkits
--dataset_names: Dataset names, you can fill in multiple, separated by commas ",", default: "assist2015"
--model_names: Model names, you can fill in multiple, separated by commas ",", default: dkt
--emb_type: Default:qid
--folds: Default: "0,1,2,3,4"
--batch_size: Default: 128
--save_dir_suffix: Add extra characters to the model storage path name, default: ""
--all_dir: Generate the configuration file of the model for this dataset, default: "all_wandbs"
--launch_file: Generated sweep startup script, default: "all_start.sh"
--generate_all: The input is "True" or "False", indicating whether to generate the wandb startup files of all datasets and models in the all_dir directory (True means: generate the startup files of all data models in the all_dir directory, False means: only the current execution is generated data model startup file), default: "False"
Example:
WANDB_API_KEY=xxx python generate_wandb.py --dataset_names "assist2009,assist2015" --project_name hawkes --model_names "dkt,dkt+"
Start Sweep
Step1: sh [launch_file] [parameter]
sh [launch_file] > [Directed log] 2>&1
- [launch_file]: required, the user submits the script of sweep to wandbs, and directs the execution output to [directed log])
- [Directed log]: Required, execute the sweep in the log
Example:
sh all_start.sh > log.all 2>&1
(You need to define the log file. )
Step 2: sh run_all.sh [parameter]
[wandb_key] sh run_all.sh [Directed log] [start_sweep] [end_sweep] [dataset_name] [model_name] [gpu_ids] [project_name]
- [Directed log]: Required, execute the sweep in the log
- [start_sweep]: Required, the start id to start a sweep
- [end_sweep]: Required, start sweep end id
- [dataset_name]: Required, dataset name
- [model_name]: Required, model name
- [gpu_ids]: Required, GPU ID
- [project_name]: optional, default: kt_toolkits
Example:
WANDB_API_KEY=xxx sh run_all.sh log.all 0 5 assist2009 dkt 0,1,2,3,4 nips2022-assist2009
Start Agents
sh start_sweep_0_5.sh
("0", "5" denote the start sweep and end sweep respectively.)
Tuning Protocol
We use the Bayes search method to find the best hyperparameter, it is expensive to run all the hyperparameter combinations. Hence, you can run the pykt-toolkit/examples/check_wandb_status.ipynb file to check whether to stop the searching. We default to stop the searching if the number of the tuned hyperparameter combinations in each data fold is larger than 200 and there is no AUC improvement on the testing data in the last 100 rounds (output “end!”).
Start Evaluation
Extract best model
def extract_best_models(self, df, dataset_name, model_name, emb_type="qid", eval_test=True, fpath="./seedwandb/predict.yaml", CONFIG_FILE="../configs/best_model.json", wandb_key="", pred_dir="pred_wandbs", launch_file="start_predict.sh", generate_all=False):
"""extracting the best models which performance best performance on the validation data for testing
Args:
df: dataframe of best results in each fold
dataset_name: dataset_name
model_name: model_name
emb_type: embedding_type, default:qid
eval_test: evaluating on testing set, default:True
fpath: the yaml template for prediction in wandb, default: "./seedwandb/predict.yaml"
config_file: the config template of generating prediction file, default: "../configs/best_model.json"
wandb_key: the key of wandb account
pred_wandbs: the directory of prediction yaml files, default: "pred_wandbs"
launch_file: the launch file of starting the wandb prediction, default: "start_predict.sh"
generate_all: starting all the files on the pred_wandbs directory or not, default:False
Returns:
the launch file (e.g., "start_predict.sh") for wandb prediction of the best models in each fold
"""
if not os.path.exists(pred_dir):
os.makedirs(pred_dir)
model_path_fold_first = []
dconfig = dict()
for i, row in df.iterrows():
fold, model_path = row["fold"], row["model_save_path"]
model_path = model_path.rstrip("qid_model.ckpt")
print(f">>> The best model of {dataset_name}_{model_name}_{fold}:{model_path}")
model_path_fold_first.append(model_path)
ftarget = os.path.join(pred_dir, "{}_{}_{}_fold_first_predict.yaml".format(dataset_name, model_name, emb_type))
if eval_test:
self.generate_wandb(fpath, ftarget, model_path_fold_first)
dconfig["model_path_fold_first"] = model_path_fold_first
self.write_config(dataset_name, dconfig, CONFIG_FILE)
self.generate_sweep(wandb_key, pred_dir, launch_file, ftarget, generate_all)
Example:
df = wandb_api.get_best_run(dataset_name="assist2015",model_name="dkt")
wandb_api.extract_best_models(df, dataset_name, model_name,
fpath="../examples/seedwandb/predict.yaml",wandb_key=wandb_key)
sh [launch_file] [parameter]
After extracting the best model, we can get the lauch file for evaluation automatically, the default filename is “start_pred.sh”. Then we can start sweep for prediction.
sh [launch_file] > [Directed log] 2>&1
- [launch_file]: required, the user submits the script of sweep to wandbs, and directs the execution output to [directed log])
- [Directed log]: Required, execute the sweep in the log
Example:
sh start_predict.sh > pred.log 2>&1
(You need to define the log file. )
sh run_all.sh [parameter]
Example:
WANDB_API_KEY=xxx sh run_all.sh pred.log 0 1 assist2009 dkt 0 nips2022-assist2009
Start Agents
sh start_sweep_0_1.sh
There are only 5 sweeps to be run without any parameter tuning in this stage, with each sweep corresponding to the evaluation of each fold of the training data. Finally, you can export the evaluation results externally or call the wandb API for statistical 5- folds results, and calculate the mean and standard deviation of each metric, i.e., mean ± standard deviation
If you want to add new models or datasets into pyKT, you can follow Contribute.