How to contribute to pyKT?
pyKT is still under development. More KT models and datasets will be added, and we always welcome contributions to make pyKT better.
Guidance
Thank you for your interest in contributing to pyKT! You can make the following contributions to pyKT:
Bug-fix for an outstanding issue.
Add new datasets.
New model implementations.
Install for Development
1、Fork the pyKT by clicking the “Fork” button.
2、Clone the repository you cloned, and switch to the dev branch (Notice: Do not work on the main branch).
git clone https://github.com/{your github name}/pykt-toolkit
cd pykt-toolkit
git checkout dev
3、Editable Installation
You can use the following command to install the pyKT library.
pip install -e .
In this way, every change made to the pykt directory will be effective immediately. The package does not require another installation again.
Push Your Codes to pyKT (Pull Requests)
After implementing the new models or fixing bugs, you can push your codes to the dev branch in your repository. Then, you can use the merge request feature to merge your codes to pyKT’s main branch.
The main branch is not be allowed to push codes (the push submission will be failed). And we will refuse the Pull Request from other branches to the main branch except for dev branch.
Add Your Datasets
In this section, we will use the ASSISTments2015 dataset as an example to show the adding dataset procedure. Here we simplify the ASSISTments2015 into assist2015 as the dataset name, you can replace assist2015 in your own dataset.
Create Data Files
1、Please create a new dataset folder in the data directory with dataset name.
mkdir -p ./data/assist2015
2、You should add the raw files of the new dataset into the named directory, like the file structure of assist2015:
$tree data/assist2015/
├── 2015_100_skill_builders_main_problems.csv
3、You need to provide the data path of new dataset to dname2paths of examples/data_preprocess.py.
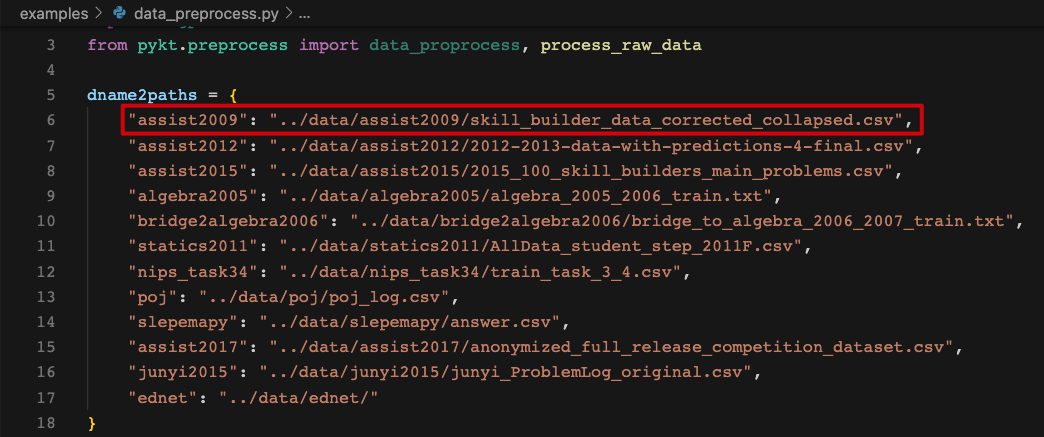
Data Preprocess File
1、Create the processing file assist2015_preprocess.py under the pykt/preprocess directory. The data preprocessing are suggested to follow the [Data Preprocess Guidelines](#Data Preprocess Guidelines). The main codes of the data preprocessing of assist2015 are as follows:
import pandas as pd
from pykt.utils import write_txt, change2timestamp, replace_text
def read_data_from_csv(read_file, write_file):
# load the original data
df = pd.read_table(read_file, encoding = "utf-8", dtype=str, low_memory=False)
df["Problem Name"] = df["Problem Name"].apply(replace_text)
df["Step Name"] = df["Step Name"].apply(replace_text)
df["Questions"] = df.apply(lambda x:f"{x['Problem Name']}----{x['Step Name']}",axis=1)
df["index"] = range(df.shape[0])
df = df.dropna(subset=["Anon Student Id", "Questions", "KC(Default)", "First Transaction Time", "Correct First Attempt"])
df = df[df["Correct First Attempt"].isin([str(0),str(1)])]#keep the interaction which response in [0,1]
df = df[["index", "Anon Student Id", "Questions", "KC(Default)", "First Transaction Time", "Correct First Attempt"]]
df["KC(Default)"] = df["KC(Default)"].apply(replace_text)
data = []
ui_df = df.groupby(['Anon Student Id'], sort=False)
for ui in ui_df:
u, curdf = ui[0], ui[1]
curdf.loc[:, "First Transaction Time"] = curdf.loc[:, "First Transaction Time"].apply(lambda t: change2timestamp(t))
curdf = curdf.sort_values(by=["First Transaction Time", "index"])
curdf["First Transaction Time"] = curdf["First Transaction Time"].astype(str)
seq_skills = [x.replace("~~", "_") for x in curdf["KC(Default)"].values]
seq_ans = curdf["Correct First Attempt"].values
seq_start_time = curdf["First Transaction Time"].values
seq_problems = curdf["Questions"].values
seq_len = len(seq_ans)
seq_use_time = ["NA"]
data.append(
[[u, str(seq_len)], seq_problems, seq_skills, seq_ans, seq_start_time, seq_use_time])
write_txt(write_file, data)
The entire codes can be seen in pykt/preprocess/algebra2005_preprocess.py.
2、Import the preprocess file to pykt/preprocess/data_proprocess.py.
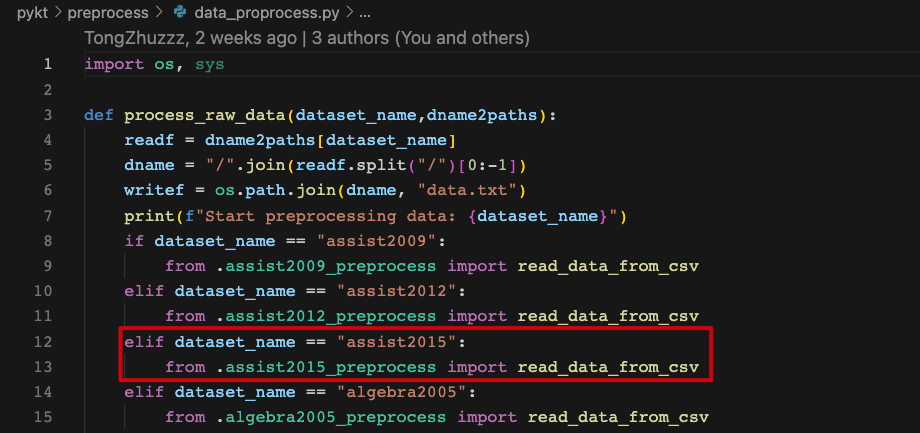
Data Preprocess Guidelines
Field Extraction
For each datset, we mainly extract 6 fields for model training: user ID, question ID (name), skill ID (name), answering results, answer submission time, and answering duration(if the field does not exist in the dataset, it is represented by “NA”).
Data Filtering
The interaction with lacks one of the five fields in user ID, question ID (name), skill ID (name), answering results, answer submission time will be filtered out.
Data Ordering
A student’s interaction sequence is order according to the answer submission time. The order will be kept consistent with the original relative position for different interactions with the same submission time.
Character Processing
Field concatenation: Use
----as the connecting symbol. For example, Algebra2005 needs to concatenateProblem NameandStep Nameas the final problem name.Character replacement: If there is an underline
_in the question and skill of original data, replace it with####. If there is a comma,in the question and skill of original data, replace it with@@@@.Multi-skill separator: If there are multiple skills in a question, we separate the skills with an underline
_.Time format: The answer submission time is a millisecond (ms) timestamp, and the answering duration is in milliseconds (ms).
Output Data Format
After completing the above data preprocessing, you will get a data.txt file under the dataset namely folder(data directory). Each student sequence contains 6 rows informations as follows:
User ID, sequence length
Question ID (name)
skill ID (name)
Answer result
Answer submission time
Answering duration
Example:
50121, 4
106101, 106102, 106103, 106104
7014, 7012, 7014, 7013
0, 1, 1, 1
1647409594000, 1647409601000, 1647409666000, 1647409694000
123, 234, 456, 789
Testing Data Format
A question may be related to multiple knowledge concepts (KCs). To make the evaluation of pyKT consistent with the real-world prediction scenarios, we train DLKT models on KCs but evaluate them on questions level. To this end, the testing data has different formats in different prediction scenarios. To better understand, we use the below example to introduce various testing data formats. There are three questions ${q_1,q_2,q_3}$, each questions are related to two KCs ${{k_1,k_3},{k_1,k_2},{k_3,k_4}}$.
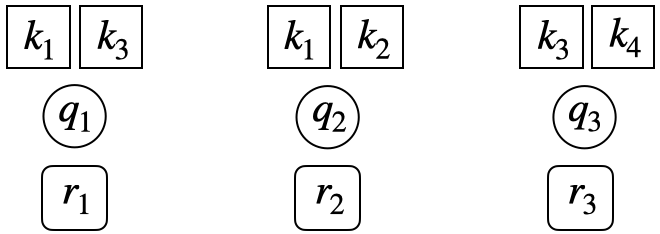
Repeat format: Similar to training data and validation data, the original question-response sequences are expanded into KC level by repeating responses multiple times when a question has more than one KCs, one for each KC.
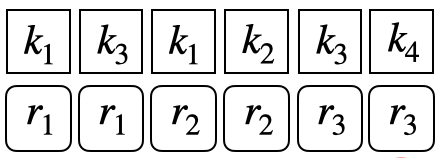
Question level format: To conduct evaluation on the question level, we split the question-response sequence into KC-response subsequence. For example, for the question $q_3$ which is corresponding to the ${k3,k4}$. A KC-response subsequence is consist of all the historical interactions and the related KC information as follows:
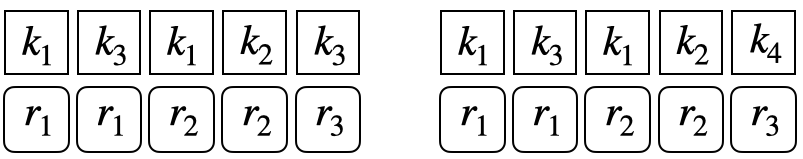
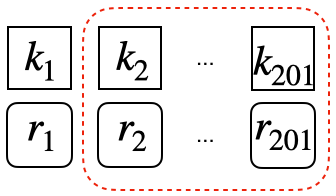
Window format: If a sequence has more than $M$ interactions, we set a sliding window to keep the sequence length is $M$. For instance, if $M=200$, the original sequence length is $201$, we select the interactions from $1$ to $201$ as final sequence:
Add Your Models
Create a New Model File
Our models are all in pykt/models directory. When you add a new model, please create a file named {model_name}.py in pykt/models.
You can write your model file using “pykt/models/dkt.py” as a reference.
Init Your Model
You need to add your model in pykt/models/init_model.py to init it by changing the init_model function.
Add to the Training Process
You should change the
model_forwardandcal_lossfunction inpykt/models/train_model.pyto add your model to the training process, you can refer to other models.Run
wandb_train.pyto train the new model
Add to the Evaluation Process
You can change the evaluate_model.py file, change the evaluate function to get the repeated knowledge concepts evaluation, change the evaluate_question function to get the question evaluation results, change predict_each_group and predict_each_group to get the multi-step prediction results of accumulative and non-accumulative predictions.